Full-spectrum LED light sources on the market
Comparison of technologies
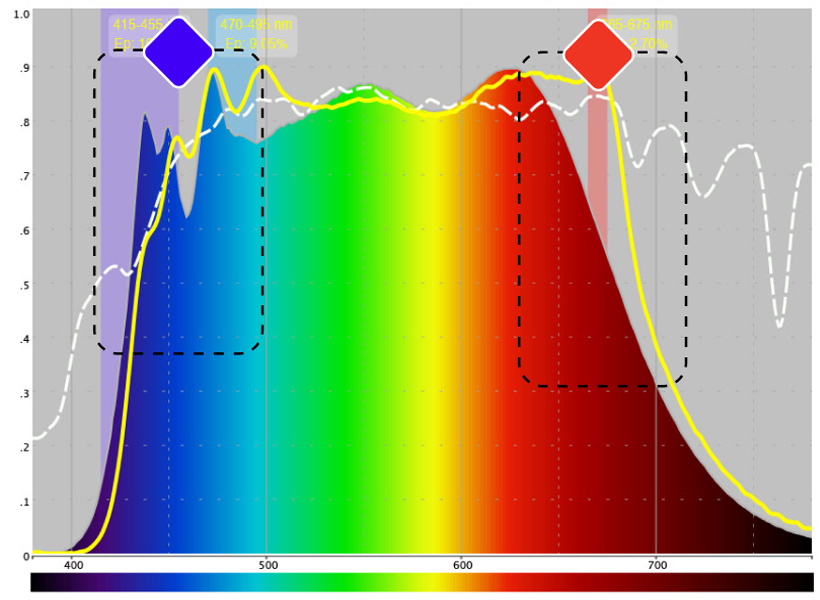
Comparison of spectral compositions
Spectrasol
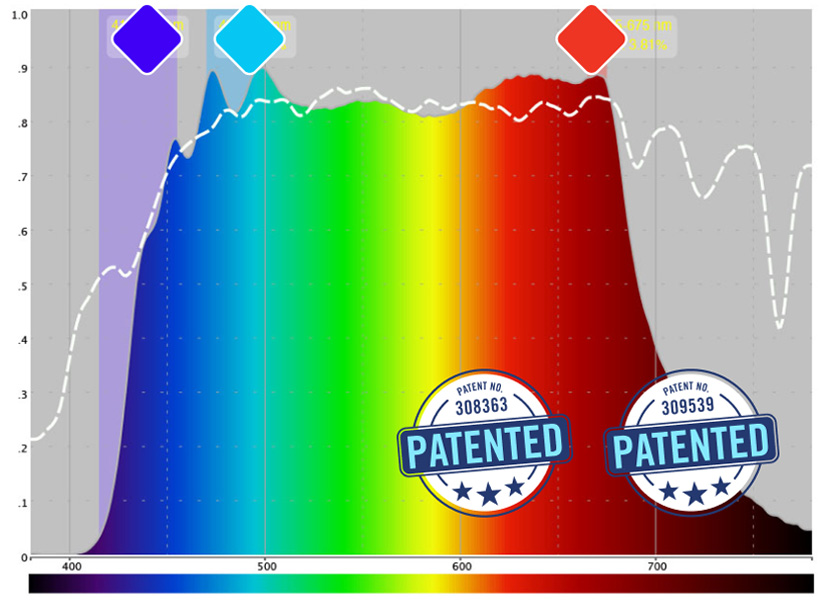
Balanced spectral composition closest to natural sunlight
Low emission of harmful blue light energy (harmful blue light range 415-455 nm)
Reduces damage to retinal cells. Protects eyesight.
Balanced cyan energy (pro-cognitive melanopic range 460-500 nm)
Supports the circadian system, regulates the body for activity during the day and regeneration at night.
Strong deep red energy (photobiomodulation range ~ 670 nm)
Compensates for harmful blue light and protects retinal cells.
Competitive solution 1
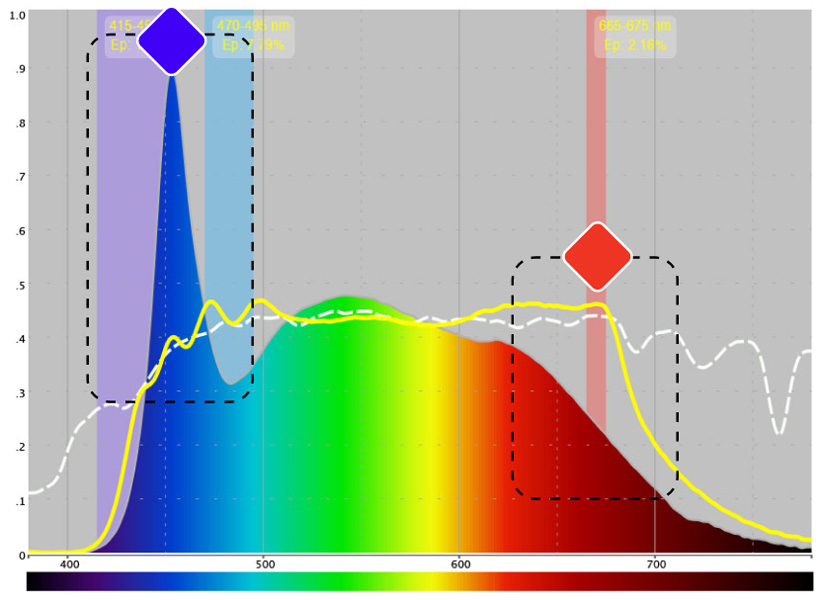
Extremely strong emission of harmful blue light energy.
High risk of retinal damage with prolonged use
Negligible representation in the red range and absence of photobiomodulatory deep red energy
Absence of regenerative potential
Competitive solution 2
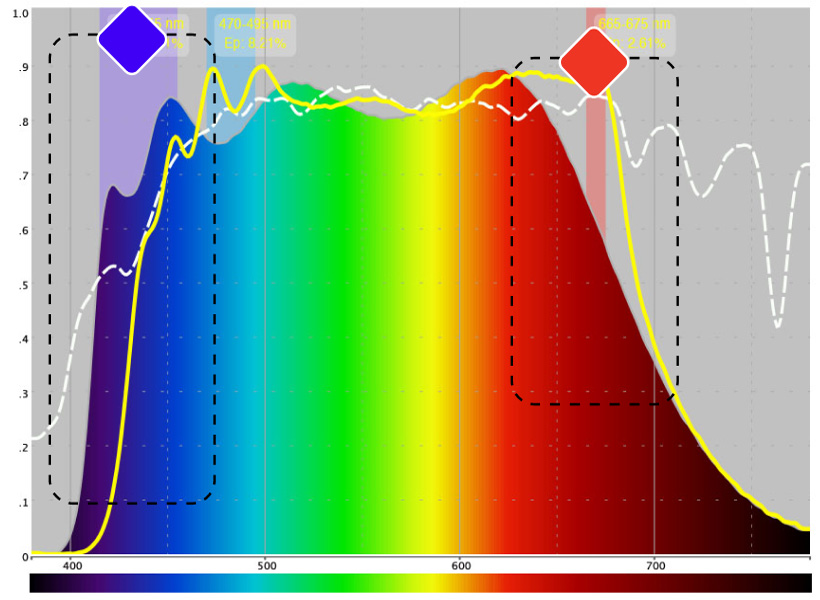
Strong emission of harmful blue light energy with excess in the violet range.
High risk of retinal damage with prolonged use
Low representation in the red range and absence of photobiomodulatory deep red energy
Absence of regenerative potential
Competitive solution 3
Emission of harmful blue light energy.
Risk of retinal damage with prolonged use
Low representation in the red range and absence of photobiomodulatory deep red energy
Absence of regenerative potential
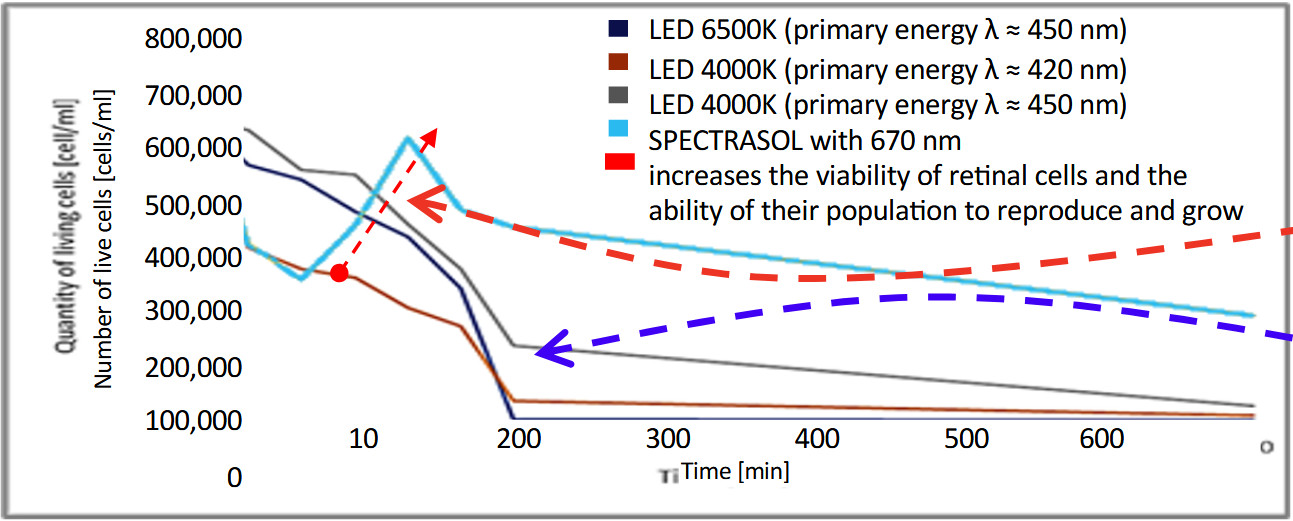
Comparison of the effects of different led sources on the retinal Cells of the eye
biomedicine and biotechnology BIOCEV.
The graph shows how the number of living retinal cells changes over time when illuminated by different types of LEDs.